Blockchain continues to grow in popularity as more businesses realize this decentralized network can transfer and store confidential information, data, contracts, and funds.
Companies in almost every industry, including healthcare, finance, real estate, supply chain, insurance, media, and entertainment, are adopting blockchain technology to strengthen their systems, implement new business opportunities, and disrupt their industries.
The secret to blockchain’s success is its strong security and speed, backed by the stable system of nodes, linking of Hashes, and proof of work (PoW).
New to blockchain? Read our Guide to Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
The Many Benefits of Blockchain
A blockchain is a new type of technical data system for storing and transferring information, data, contracts, goods, or currency. The system uses a non-centralized network to create a digital ledger of transactions.
Users are free to engage with the ledger through Cryptography, the operator allowing these transactions to occur. Because it’s decentralized, the transaction speed is breakneck. Unlike networks made by a single entity, blockchain enables computers to collaborate.
A blockchain is built in a string of “blocks” linked by Hash, all of which are unique and grows continuously as new blocks are proved and added to the security chain. Cryptography enables and protects the blockchain network.
Blockchain is being used across various industries to speed transactions and secure information and data against malicious attacks and theft. It has even made it possible for innovative startups to raise funds in ICO.
Many people new to blockchain worry about the security and recovery of information. In the event of a catastrophe, attack, or crash, blockchain users can quickly recover lost data from the digital ledger stored in a decentralized structure across multiple nodes.
If someone were to attempt unethical business within a blockchain by modifying a ledger to embezzle funds, that would not occur. If a hacker were to tamper with a block, PoW would still require half of all nodes within the blockchain network to verify the modification. Such an event is improbable, as the blockchain’s security is secured in the network’s widespread distribution of nodes.
Once a block has been confirmed and added to the blockchain, changes are no longer permitted unless at majority rule votes to do so. This added security level protects the blockchain from hacking and tampering by anyone, including its own administrators. This heightened security makes blockchain priceless for organizations working to produce a secure system for information, data, currency transfer, and sharing.
Below are just four of the esteemed benefits for engineers, companies, and individuals interested in implementing blockchain technology.
1. Blockchain Creates A Trustworthy, Secure System
Blockchain technology finds its strength and security in the structure that makes it possible for users to verify and check the blockchain community’s additions, bypassing traditional third-party authorization and confirmations. Such structure protects each blockchain from hacking attempts, attacks, crashes, and any transaction attempt not authorized by its administrators.
Blockchain’s superior security is found in its decentralized structure and tamper-proof Hash, protecting data and currency within blocks. Digital ledgers make it easy to identify changes in the blockchain, and modification is only possible with the support of large, widespread teams.
2. Blockchain Facilitates Ultimate Transparency
Blockchain’s structure is built as a distributed ledger that ensures complete privacy and control of all data, information, and transactions to the network users. Any changes or modifications to the blockchain are always completely transparent and accessible to the public. The use of a single publically available digital ledger makes it easy to spot modifications or hacking attempts while also reducing the messiness associated with systems containing multiple ledgers.
3. Achieve Faster Transactions with Blockchain
Markets that work with digital documentation, including contracts and money transfers, often experience long time periods to process and complete transactions. Traditional transfers between banks and countries often take several days to clear before payment and data can be received.
Enter blockchain. Blockchain not only reduces that long wait to just a few minutes, but it can be completed any time of day, seven days a week, thanks to the decentralized node structure.
The implications of instant transfer offer an opportunity for disruption across countless industries and have the potential to significantly reduce both costs and workload, increasing the efficiency and automation of routine transactions.
4. Blockchain Reduces Transaction Costs
What once involved costly fees can now be completed at a fraction of the price with the decentralized blockchain community’s help. The Euro Banking Association (EBA) recently released a report on Crypto technologies, predicting a future of reduced governance and audit costs, freeing businesses to innovate and reach the market faster.
The growth of blockchain technology improves efficiency and transparency across businesses while reducing costs and removing time-consuming checks. We are likely to see growth in the healthcare industry that will benefit from more comprehensive and secure medical records infused with patient-reported wearable device data.
Also, watching is the supply chain industry, which will benefit from quicker and more reliable goods transfer and tracking—the entertainment industry is already finding new ways to complete transactions for digital downloads and streaming.
Real-World Cases: Blockchain At Work
Blockchain has obvious applications in the technology space. Due to its speed and security, its use cases go far beyond tech, touching industries including, but not limited to: healthcare, supply chain, media, entertainment, finance, real estate, insurance, and even public government agencies.
We can certainly expect to see significant growth in blockchain across the board as cryptocurrency slowly becomes just as ubiquitous as past technological innovations like touch screens and wireless data transfer.
Blockchain: Healthcare and Supply Chain Industries
As wearable and consumer reported health tracking devices to continue to grow in ability and reach, it’s become necessary to connect that valuable daily data to medical records.
Blockchain has the ability to manage and combine medical data safely, providing a wealth of knowledge for physicians and practitioners, and has the potential to significantly contribute to curing disease, understanding unknowns, and ultimately, saving lives.
Using the same framework of secure data management and transfer, Skuchain and Factom are both working on using blockchain to securely and systematically manage the transfer of goods as they transition ownership in factories, warehouses, transportation hubs stores. Such innovation paired with the growth of eCommerce can disrupt shopping and streamline consumer purchases like never before.
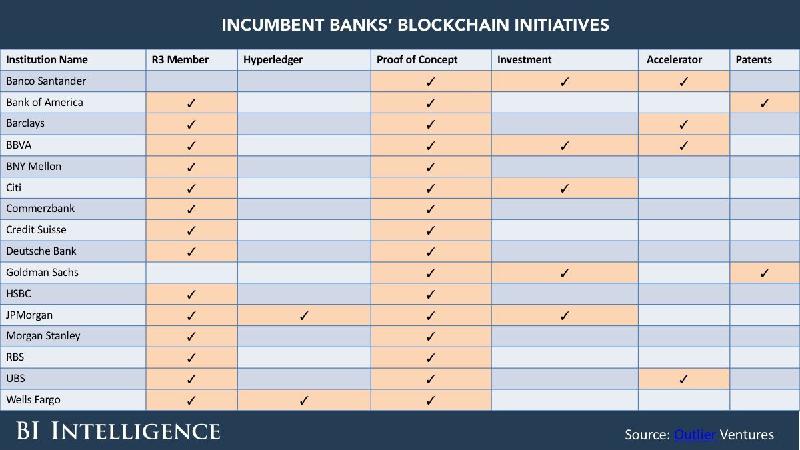
Blockchain In the Financial Industry
Banco Santander, a Spanish banking group, is actively testing and researching the use of blockchain technology as a more cost-efficient option for secure international currency transfers. Blockchain may be the answer they’ve been looking for to reduce the cost of transfers by capitalizing on blockchain’s tamper-resistant blocks.
Barclays, a British banking and financial services company, was successful in one of the first blockchain-based finance deals in late 2016 with a blockchain system that reduced the time to execute a letter of credit from days of manual paperwork to just four hours.
Blockchain’s Humanitarian Help
Blockchain was at the heart of a humanitarian effort led by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood, a big data firm, Datarella, and the United Nations’ World Food Program (WFP) 10,000 cryptocurrency vouchers to Syrian refugees last year.
Those vouchers were, in turn, used to purchase much-needed food and medicine for refugees living without. Blockchain money transfers can bypass government regulations and securely transfer funds at a fraction of the cost, a tool that can potentially save thousands of lives around the world.
Blockchain is doing its part in helping further connect the world by providing anyone with a smartphone the opportunity to buy and sell goods and services. BitPesa, for example, uses blockchain technology to reduce the cost and increase the security of cryptocurrency transfers to and from African villages.
Blockchain: Media and Entertainment
Instant and secure payment transfers are extremely desirable in the fast-paced media and entertainment industries. We’ve already witnessed, Publiq making it possible for freelance writers and content creators to sell their services over blockchain, and media and Internet giant, Comcast, has begun selling advertising space over secure blockchain networks.
A new internet-based game called Cryptokitties is working to bring blockchain technology mainstream by teaching users how to buy and sell Bitcoin and Ethereum cryptocurrency through an interactive game of collecting and raising virtual feline pets.
Blockchain: Insurance and Real Estate
The security of the blockchain is certainly attractive to industries dependent on contracts and legal documents.
Deloitte is particularly interested in the blockchain’s impenetrable bonds within the blockchain that could enable secure internet-based contracts and claims, thereby eliminating invalid claims.
We can expect to see blockchain applications in the real estate industry as well, as decision-makers are likely to take advantage of quick and secure form processing to complete property sales more efficiently.
Opportunities for Blockchain in Government
Notorious for absolute security, many government agencies still require physical paper documentation, a fact that continues to force upstanding citizens to stand in line at the Department of Transportation (DOT) and wait in long phone queues to confirm identity.
Blockchain could be the secure system federal agents have been searching for, making it possible to store and access information including securely, but not limited to: Birth and death records, marriage licenses, criminal records, business licenses, property transfers, social security, and state identification cards, taxes and even voting.
In the instance of property (both physical and intellectual) transfer, blockchain ledgers are invaluable for their clean and clear outlines of each transaction over property lifetime.
Using smart contracts engineered to autofill data and confirm identity, blockchain may eventually execute and manage complex contracts and legal procedures systematically, without the need for human input. Such use of blockchain could decrease wait times, eliminate human error, and free agency employees from mundane tasks, allowing them to innovate.
What Are Dapps?
The new blockchain architecture called Dapp stores data and source code in a decentralized manner distributed in the blockchain, ensuring that applications are always online.
For an application to be considered a Dapp (pronounced Dee-app), it must meet the following criteria – otherwise, it’s considered a hybrid.:
1. Open-source. The software application must be autonomous, open-source, and without a governing board or party managing cryptocurrency shares. The application is free to grow and develop at will, but blockchain users must first vote on changes.
2. Publically accessible, decentralized blockchain. The software application must store all data and records using Cryptography in a publicly accessible, decentralized blockchain, thus increasing nodes’ spread to ensure ultimate security.
3. Cryptographic tokens. The software application must process any payments through cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin or another Altcoin native to the application, and the cryptocurrency must be essential to access the software. If a company accepts support or contribution from farmers or miners, payment should only be dispersed in cryptocurrency tokens.
4. Verification for growth. The software application must follow a standard cryptographic algorithm to verify blocks and generate cryptocurrency for node growth. Bitcoin, for example, follows the PoW algorithm.
Classification of Dapps
There are different variations of Dapps depending on their association or non-association with a current blockchain.
Type I Dapps are decentralized applications that maintain their own blockchain. This type of structure is followed by the widely known Bitcoin, as well as Litecoin.
Type II Dapps are decentralized applications that use the existing blockchain of a type I dapp and are themselves protocols requiring cryptocurrency to run. Omni Protocol is a more popular type II dapp protecting blockchain.
Type III Dapps are decentralized applications built upon protocol in place by a type II dapp and require cryptocurrency to function. SAFE Network is an excellent example of a type III dapp. They use the Omni Protocol type II dapp to issue ‘Safecoins’ that can be exchanged to acquire distributed file storage.
What qualifies a software application as a Dapp?
SaaS software and cloud-based software solutions continue to set trends for lightweight and agile tech businesses. Although Dapps have the ability to be applied to any industry, those currently capitalizing on dapp include Law, accounting, music, travel, and finance.
A software application or program qualifies as a dapp if it meets the following four criteria.
1. Open source. The software application must be autonomous, open-source, and without a governing board or party managing cryptocurrency shares. All data, contracts, currency, and records must be stored using secure Cryptography and permanently stored in a publicly available, decentralized blockchain.
2. Cryptocurrency. The application must generate a standard cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or a token native to its system and abide by a standard algorithm for operation. The software application must require the use of its chosen cryptocurrency for access, and any payments made to any miners, farmers, or blockchain users should always be executed in cryptocurrency tokens.
3. Open to an ICO. The application is free to distribute some or all of its tokens at the beginning of its operation in an Initial Coin Offering (ICO).
4. Majority consensus. While the application is free to grow and improve its own system, any modifications to the protocol must be decided upon by the blockchain users.
If that’s a bunch of gobbly gook tech talk to you, let us sum it up in layman’s terms.
Dapps decentralize a software application across the blockchain, moving control from a single leader (a founder, CEO, or board) to all blockchain users.
Doing such establishes equality between users and ensures safe, secure, and transparent dealings.