Fourth Industrial Revolution enthusiast and passionate about Analytics, Startups, and…
In the past months, the term NFTs has entered the mainstream space because of the excessive amount of money transactions around them. In February 2021, an NFT of the popular Nyan Cat GIF sold for 300 ETH (around USD 590,000) in an online auction. ETH is the cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain, which is the most commonly used blockchain for NFTs.
In March, the famous artist Beeple sold an NFT for USD 69 million. His work of art: a JPG collage titled «Everyday: The First 5000 Days» consisting of the futuristic digital images that he created each day from May 1st, 2007, all the way to January 7th, 2021. Why would people pay these prices for digital content that they can see for free on the internet? And what can be the real-world applications of NFTs?
What is a Non-Fungible Token (NFT)?
Non-fungible Token (NFT). Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs), translated into Spanish Non Fungible Tokens. It is a cryptographic token that represents a single asset within a blockchain. They can be entirely digital assets or tokenized versions based on real-world assets. NFTs are not interchangeable with each other, so they function as proof of authenticity and ownership within the digital world.

We must first understand what fungibility is and how blockchain technology works.
Fungibility
A fungible good is anything that we spent with use and time, can replace it with other of the same value. For example, would you prefer two $5 bills or one $10? Surely you will tell me that it does not matter. In the end, you will get the same value with any option. It means bills can be replaced by another (or others) of the same weight since the money is fungible. The same applies to cryptocurrencies like bitcoin (BTC) or ether (ETH).
On the other hand, art is not fungible; its unique characteristics make it irreplaceable; however, its value is subjective. That is why we see abstract paintings auctioned for millions of dollars. Some collectors may find a deal in them, but it is not the same for everyone. Thus we come to the NFTs, like art. They are collectible assets (not expendable) in digital format.
Blockchain technology and NFTs
The other key aspect is that NFTs are tie to a blockchain. This technology registers transactions on a digital ledger. Everyone on the network has a copy of these transactions; they are encrypted and structured in a series of «blocks.» Blockchain provides a digital, non-hackable certificate of ownership, and there can only be one owner at a time.
How do NFTs work?
There are various schemes for the creation and issuance of NFTs. ERC-721 is the most prominent standard for issuing and trading non-fungible assets on the Ethereum blockchain. A more recent standard, ERC-1155, allows a single contract to contain both fungible and non-fungible tokens, opening new possibilities.
Standardization in the issuance of NTFs allows a greater interoperability degree, which means that the owner will effortlessly transfer that unique asset between different applications.
NFTs are for sale through different platforms, such as Marketplace, OpenSea, or Descentraland. Users make payments through Crypto Wallets compatible with platforms such as Coinbase Wallet or MyEtherWallet. Once they acquire the NFT, it remains at an address on the blockchain where you can view them.
A digital art collector may have a JPG file that everyone can see online, but only he or she will have the certificate proving its authenticity; this accredits you as the sole owner of your NFTs.
It is essential to clarify that the NFTs do not confer the digital asset’s intellectual property. Just as we cannot duplicate a book, we are not the author, even if we have acquired it.
NFTs Early Days
The NFTs had their first appearances during 2017.
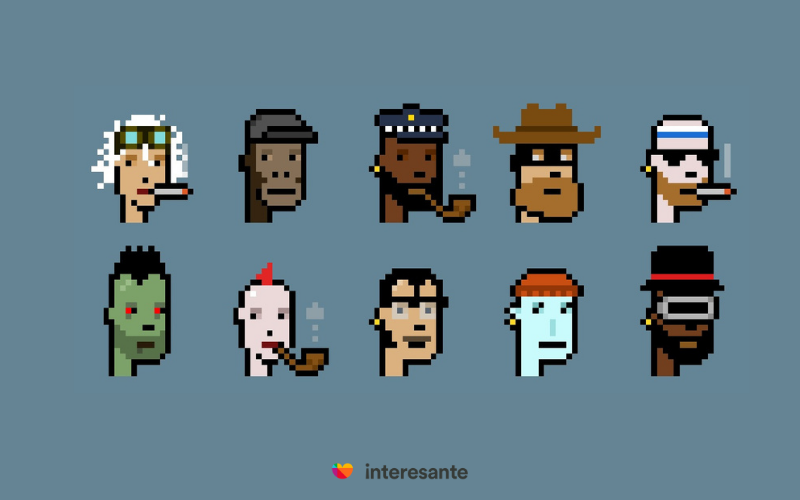

In June 2017, Larva Labs, an American studio, launched a collection of 10,000 crypto-collectibles known as Cryptopunks. Each of these punks is unique and generated through a computer algorithm. They originally released for free to anyone with access to the Ethereum blockchain. In February 2021, CryptoPunk #7804 sold for 4,200 ETH (roughly $7.5 million USD).

In October 2017, the Canadian company AxiomZen (now Dapper Labs) launched a blockchain-based game called CryptoKitties, with kittens as the protagonists. Each has a code that contains several different attributes. People can put two cats together to generate new offspring and develop new generations.
Each new kitty has a unique code, just as human DNA is not replicable. This digital scarcity concept is new; digital assets generally can be copied and accessible to everyone online. The game then increases in popularity in the following months, and in September 2018, a Cryptokitty sold for 600 ETH (approximately USD 170,000 at the time).
NTFs in the Sports and Music Industry
Dapper Labs (CryptoKitties’ creators) partnered with the NBA and launched their crypto-collectibles platform NBA Top Shot in October 2020. Similar to baseball cards, collectors can buy packs of virtual cards containing video highlights from NBA games.

These packs, which usually sell out fast, can range from $9 to $230 depending on the rarity of the cards they may contain. In less than a year, the platform has seen more than USD 200 million in sales.
Collectors are willing to pay high prices to resell these NFTs for a profit.
An NFTs of the NBA with a LeBron James’ dunk sold USD 208,000 in February 2021.
Kings of Leon is the first band to use NFTs to release a music album. The launch was in March 2021, earning more than USD 2 million. The band released three NFTs or tokens: limited edition albums, golden tickets to future shows, and unique works of art. The album token costs $50 and could be purchased up to 2 weeks after release.
After that, no more album tokens will be produced, thus creating digital scarcity. The golden tickets are 18 in total, and they provide the owner with four front-row seats in any future concert of each band tour, as well as a VIP experience that includes an opportunity to hang out with the band. This fact is truly a game-changer for the music industry and can leverage by struggling artists.
Criticism and the possible applications of NFTs in the future
NFTs have been subject to critiques from all kinds of perspectives. One of the most common is that of carbon footprint. To record a new transaction on a blockchain, computer processors have to solve a series of mathematical problems. This action consumes high quantities of electricity.
If Ethereum were a country, its energy consumption would be roughly the one of Nigeria. Add Bitcoin to the equation, and the energy consumption is similar to the one in Norway.
NFTs are emerging in the mainstream of the internet as crypto-collectibles, but their future use can go much further. For example, memberships, clubs, and different organizations could grant membership for NFTs, proving benefits.
When a person uses their membership, the token will be guaranteed by an authentication whenever they use it. Moreover, media and content creators could grant voting rights to their token holders. This activity could allow them to help decide what kind of content to create next.
Non-fungible Token (NFT). Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs). It is a cryptographic token that represents a single asset within a blockchain. They can be entirely digital assets or tokenized versions based on real-world assets. NFTs are not interchangeable with each other, so they function as proof of authenticity and ownership within the digital world.
There are various schemes for the creation and issuance of NFTs. ERC-721 is the most prominent standard for issuing and trading non-fungible assets on the Ethereum blockchain.
NFTs are for sale through different platforms, such as Marketplace, OpenSea, or Descentraland.
Users make payments through Crypto Wallets compatible with platforms such as Coinbase Wallet or MyEtherWallet.
The artist Beeple, Lava labs, Dapper Labs, the NBA, the King of Leon group.
What's Your Reaction?
Fourth Industrial Revolution enthusiast and passionate about Analytics, Startups, and Sustainable Development.